Lateral Flow Assay Uncut Sheets
Lateral Flow Assay Uncut Sheets uncut sheets are specialized materials.
The production of lateral flows involves the precise placement and alignment of components on the Lateral Flow Assay Uncut Sheets, ensuring proper flow and accurate test results. Additionally, automated equipment frequently handles the large sheets and executes precise cutting and assembly processes. Once the lateral flow assay test strips are cut from the uncut sheet, additional steps, including drying, packaging, and quality control testing, are undertaken. These steps are carried out before distributing the strips as ready-to-use diagnostic kits.
What is LFA ?
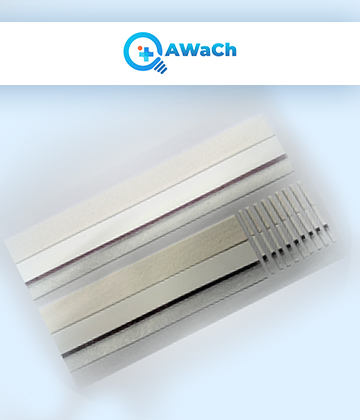
They consist of a large sheet or roll of the various components that make up a lateral flows, including the nitrocellulose membrane, sample pad, conjugate pad, absorbent pad, and backing card.
Lateral Flow Assay uncut sheets serve as a precursor to the individual lateral flows test strips that are commonly seen in in vitro diagnostic kits.
Firstly Manufacturers typically purchase these uncut sheets and then customize them according to their specific test requirements, including the target analyte, detection method, and desired performance characteristics.
Secondly The uncut sheets allow for flexibility in the manufacturing process, as they can be customized to produce lateral flow test strips with different configurations and specifications.
Thirdly Manufacturers can cut the sheets into smaller strips of specific dimensions, apply additional coatings or reagents, and assemble them into the final test format.
Uncut sheets offer efficiency in large-scale lateral flow assays test production, enabling high-volume manufacturing and customization based on specific test requirements. These sheets play a crucial role in streamlining the production of LFAs for various applications, including medical diagnostics, veterinary testing, food safety, and environmental monitoring. QAWach Bio also manufactures uncut sheets for a number of its lateral flow assay diagnostic tests.
Specialized materials, found in large sheets or rolls, comprise all the essential components of a lateral flow assay. These components consist of the nitrocellulose membrane, sample pad, conjugate pad, absorbent pad, and backing card. Manufacturers using these uncut sheets as the foundation for creating individual lateral flow test strips, which are frequently part of in vitro diagnostic kits.
Strength:
The strength of LFAUS lies in their versatility and efficiency. Manufacturers have the capability to customize these sheets to meet specific test requirements. This allows for the production of lateral flow test strips with different configurations and specifications. Consequently, this adaptability streamlines the manufacturing process and facilitates high-volume production.
Advantages:
LFAUS Sheets offer several advantages in the production of diagnostic test strips. Moreover, they enable efficient large-scale manufacturing, which is crucial for meeting the demand for diagnostic tests in various fields, including medical diagnostics, veterinary testing, food safety, and environmental monitoring. Additionally, these sheets provide flexibility for customization, allowing manufacturers to tailor test strips to their exact needs.
Recognitions:
Uncut sheets play a vital role in the streamlined production of LFA, contributing to the accessibility of diagnostic testing in diverse applications. They are recognized for their role in improving manufacturing efficiency and enabling the customization of lateral flow test strips.
Innovation:
Manufacturers utilize innovative processes to cut and assemble LFA test strips from uncut sheets. Through automated equipment, precision in cutting and assembly is ensured, guaranteeing the proper flow and accurate test results. Notably, QAWaCh Bio is among the innovators in this field, producing uncut sheets for various lateral flow assay diagnostic tests. Their commitment to efficient and customizable manufacturing significantly contributes to the advancement of diagnostic technologies.
